Resistive Random-Access Memory
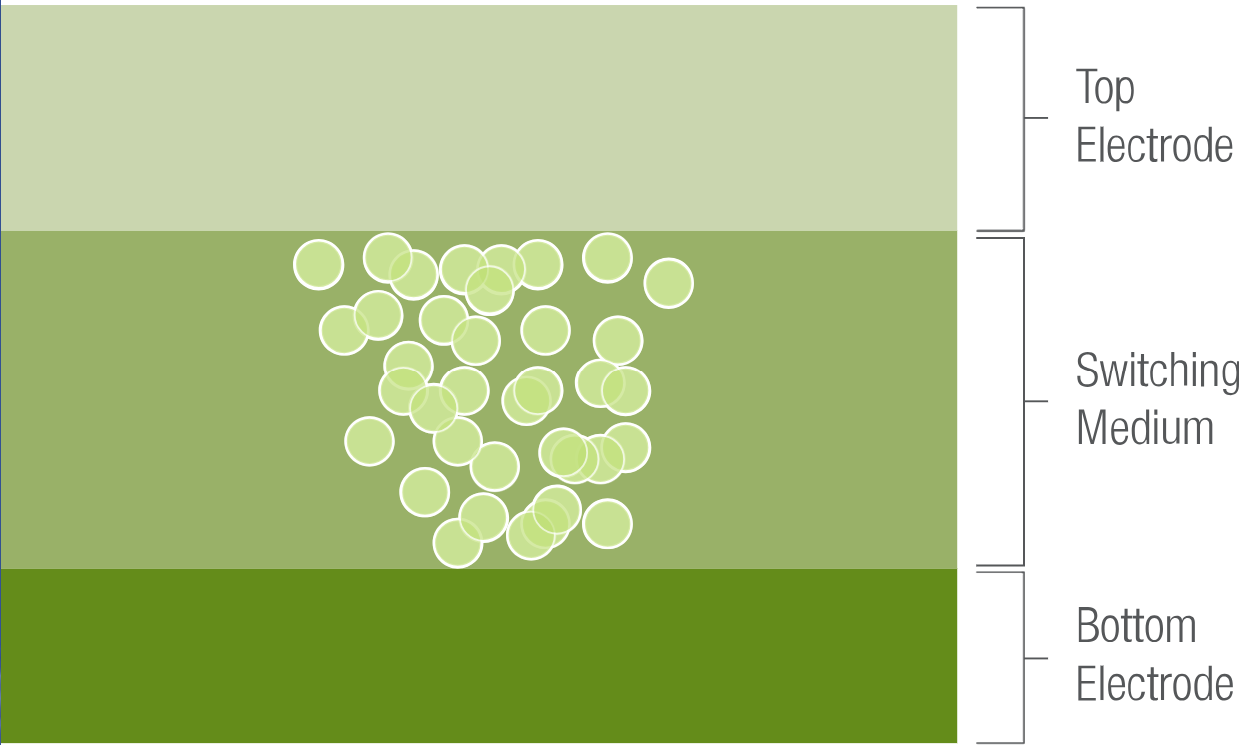
Resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) is based on a simple three-layer structure of a top electrode, switching medium and bottom electrode (Figure 1). The resistance switching mechanism is based on the formation of a filament in the switching material when a voltage is applied between the two electrodes. There are different approaches to implementing ReRAM, based on different switching materials and memory cell organization, making ReRAM highly adaptable for use as multiple-time programmable (MTP), few-time programmable (FTP) and one-time programmable (OTP) non-volatile memory applications.