Crossbar Tries to Secure Embedded ReRAM IoT Market
How CrossBar positions ReRAM for IoT with strong resistance to content-detection threats.
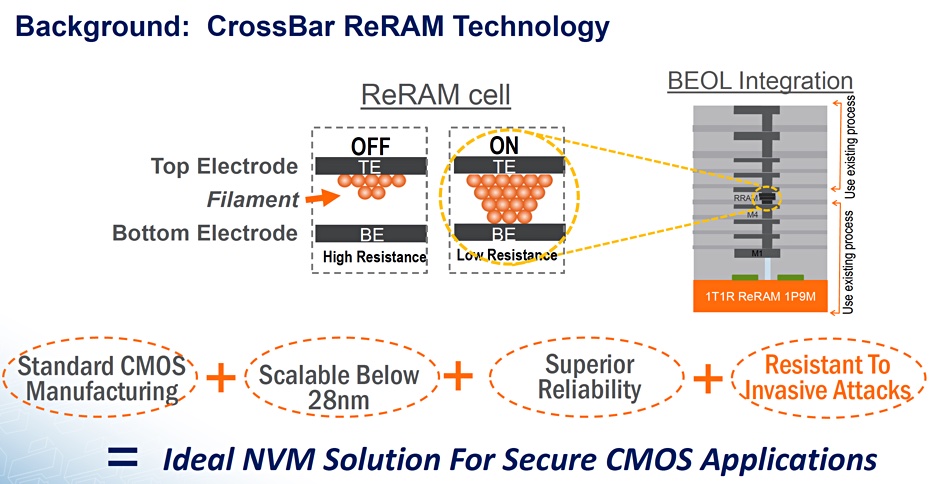
How CrossBar positions ReRAM for IoT with strong resistance to content-detection threats.

CrossBar’s Resistive RAM technology is now being offered for use in memory applications requiring higher levels of content security.
CrossBar and CertiK present EMPC live demos and the Daric chip at TOKEN2049 Singapore.
CrossBar will debut the Daric chip and EMPC live signing at TOKEN2049 Singapore.
Why ReRAM’s physical characteristics provide resilience against invasive attacks.
Bill Wong interviews CrossBar’s Sylvain Dubois on storage innovation.
Announcement on new usage modes broadening embedded ReRAM applications.
Coverage of CrossBar’s security angle for embedded ReRAM in compute.
Process and yield considerations for emerging NVM.
Introductory analysis of ReRAM as an embedded alternative.
How ReRAM and PUF combine to create a unique and inexpensive security solution. By Katherine Derbyshire.
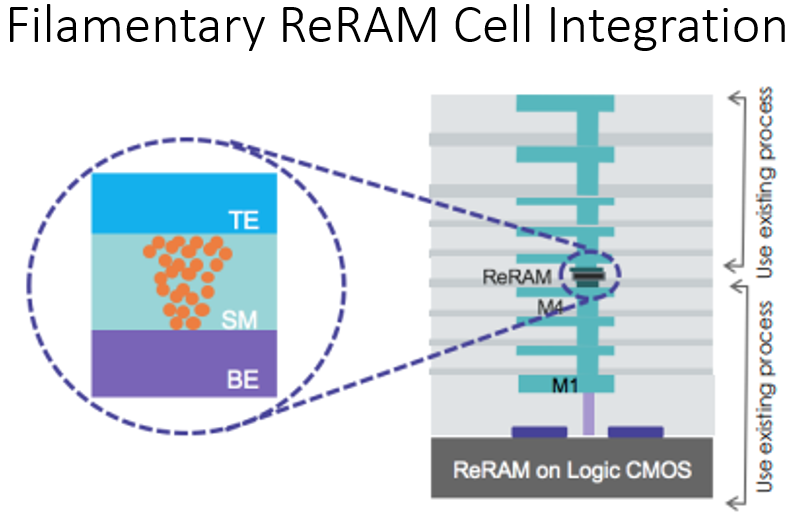
Why moving less data is critical; implications for memory architectures. By Brian Bailey.
Emerging memories in R&D and their potential impact on compute architectures. By Mark LaPedus.
Positioning ReRAM around near-invincibility to external content-detection threats. By Chris Mellor.
ReRAM offered for applications requiring higher levels of content security. By Chris Mellor.
Ashish Pancholy on advantages of ReRAM for secure applications. By Amelia Dalton.
Using ReRAM to implement PUFs and harden systems. By William G. Wong.
Highlighting resistance to reverse engineering and physical attacks.
CrossBar’s Resistive RAM technology for secure memory applications.
Overview of CrossBar’s FTP/OTP ReRAM announcement.
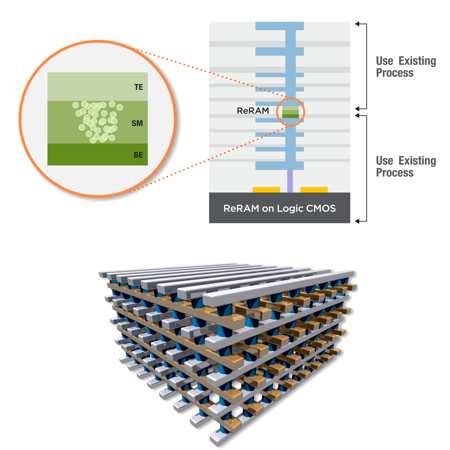
Few-Time and One-Time Programmable Memory Applications Using ReRAM.
PUFs as a means of embedding security in hardware.
Potential of ReRAM and production status. By Gary Hilson.
Mentions CrossBar’s new ReRAM application for hardware security.
ReRAM suited for a new class of PUF applications.
Using ReRAM PUFs to generate cryptographic keys in secure computing.
Precision manufacturing for next-gen memories. By Brandon Lewis.
Using ReRAM to create PUF cryptographic keys.
Imbalance between compute and data access spurs new RAM tech. By Michael Feldman.
Advances that improve memory for neuromorphic systems. By Michael Feldman.
Update on resistive RAM memory features and developments.
Trends in storage demand, NVMe, computational storage, and security. By Tom Coughlin.
Opportunities for RRAM and FRAM amid scaling slowdowns. By Tom Coughlin.
HDD, tape, and capacity trends for the coming decade. By Tom Coughlin.
Insights from GTC and AI Hardware Summit on memory tech. By Tom Coughlin.
Recap of a workshop on a multimillion-dollar cybersecurity project.
ReRAM’s status and challenges as an “emerging” memory. (EE Times Asia)
City-level recognition list featuring local startups. (The Tech Tribune)
VentureBeat overview of new memories. By Chris Angelini.
A look back at ReRAM progress and prospects. (SemiWiki, Bernard Murphy)
RRAM’s role across AI, IoT, and big data. (IDST)
Briefing 7: CrossBar. (Storage Switzerland)